Game Theory
Game Theory
Level: AS Levels, A Level, GCSE – Exam Boards: Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, IB, Eduqas – Economics Revision Notes
Game Theory
Game Theory is the study of interactions based off strategic thinking, where one player’s decision is dependent upon the moves of its opponent. Economists use Game Theory to understand the behaviours in an oligopoly firm.
Nash Equilibrium occurs when each player will gain nothing by changing strategy, given the choices of its opponent. It is possible that at Nash Equilibrium, both players could gain from co-operation.
Dominant Strategy is when one choice yields a better result than the other options available.
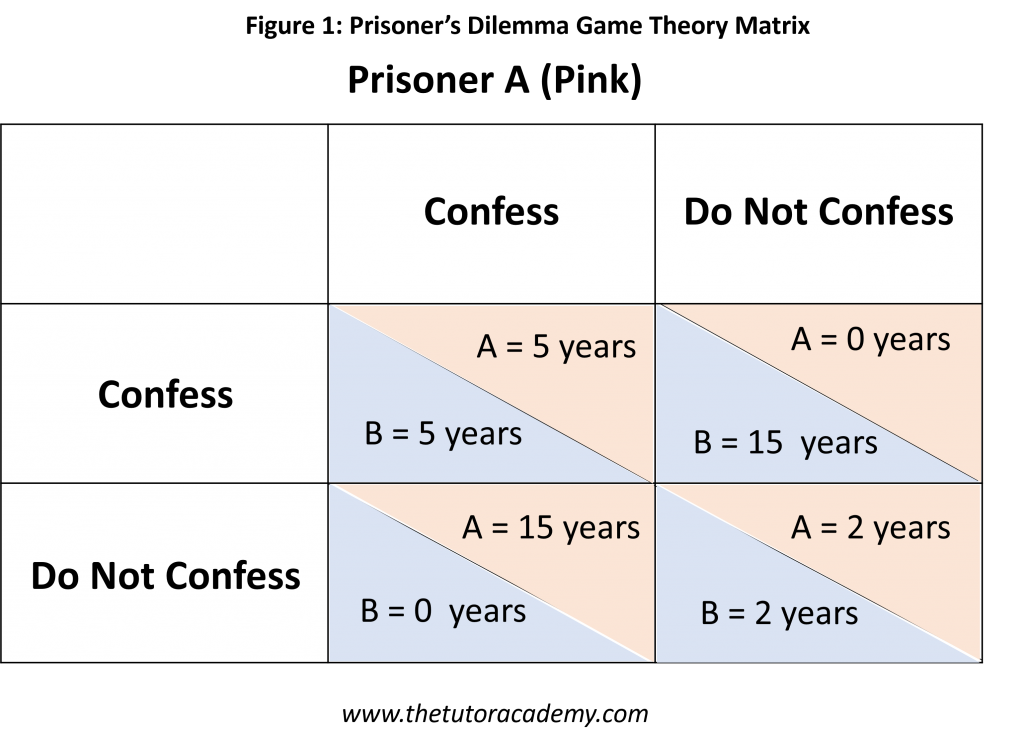
Prisoner’s Dilemma
Prisoner’s Dilemma is a model used to establish whether two independent parties choose to collaborate in a given situation or act as opponents. Usually, the highest reward for each party is gained when both parties choose to cooperate.
[2 examples + explanations]
- Two prisoners engaged in a crime; the police have caught them and they are now being held hostage.
- They have the option to either confess to the crime or remain silent.
- If both confess, they will get a sentence of 5 years.
- However if neither confess, they will only get a sentence of 2 years.
- If Prisoner A confesses but Prisoner B remains silent, Prisoner A will receive a 15 year sentence while Prisoner B receives no sentence.
- Alternatively, if Prisoner B confesses but Prisoner A remains silent, Prisoner B will receive a 15 year sentence while Prisoner A receives no sentence.
- The dominant strategy for both players is to confess; at best, they’ll get no sentence but at worse, they’ll receive 5 years each.
- The Nash Equilibrium is (Confess, Confess).
Cartels are then formed as a result of firms acting as one through an agreement.
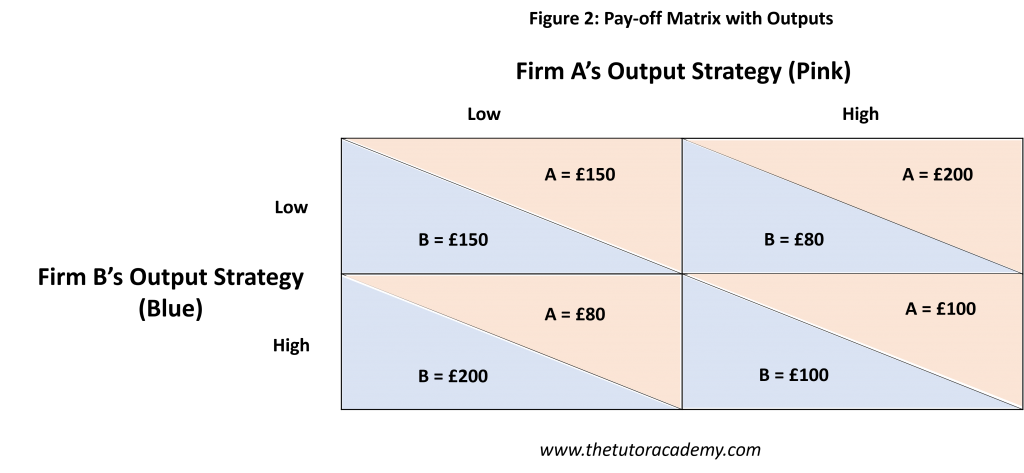
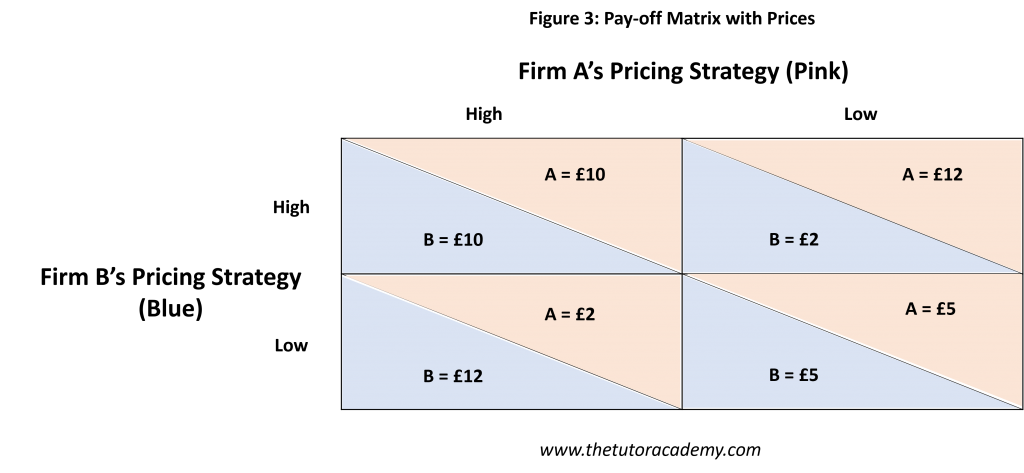
Pay-off Matrix
A Pay-off Matrix is a table displaying the options available to players of a game. It is two-firm, two-outcome model.
Different Pricing Strategies
1. Price Wars
This occurs when one firm reduces their prices to maximise the amount of products sold, leading to greater profit being made. This results in the competitor firm losing market share and making less profit as they will make less sales due to their prices being higher. Consequently, they want to also cut their prices. This starts a price war as now the original firm wants to reduce their prices further.
2. Price Leadership
In a market where a dominant firm exists, they will act to change prices as they know other firms will follow. This is because price wars and other forms of retaliation are likely to occur within this market. As a result, the dominant firm becomes the established leader.
3. Predatory Pricing
This is usually a short-term measure which involves a firm cutting prices below the average cost of production to push its competitors out of the market. Once the other firms have been forced out of the market, it will raise its prices again to make supernormal profits.
4. Limit Pricing
This occurs when firms cut prices to deter entry of other firms into the market. Competitors looking to enter the market will be discouraged as they would not be able to compete with the higher-cost firms already existing within the market.
Non-Price Competition
This is when firms compete without changing its prices. Instead, it uses other methods to increase sales, such as:
- Advertisement
- Product Quality
- Customer Loyalty
- Free Gifts
Quick Fire Quiz – Knowledge Check
1. Define ‘Game Theory’ (2 marks)
2. Define ‘Nash Equilibrium’ (2 marks)
3. Define ‘Dominant Strategy’ (2 marks)
4. Using an example, explain what a ‘Pay-off Matrix’ is (6 marks)
5. Explain what the ‘Prisoners Dilemma’ model is (4 marks)
6. Identify and explain an example of Prisoner’s Dilemma (4 marks)
7. Identify what a Cartel is (2 marks)
8. Identify and explain four different Pricing Strategies (8 marks)
9. Explain what ‘Non-Price Competition’ is (4 marks)
Next Revision Topics
- Oligopoly
- Concentration Ratios
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic Competition
- Perfect Competition
- Efficiency
- Monopsony
- Price Discrimination
- Contestability
A Level Economics Past Papers